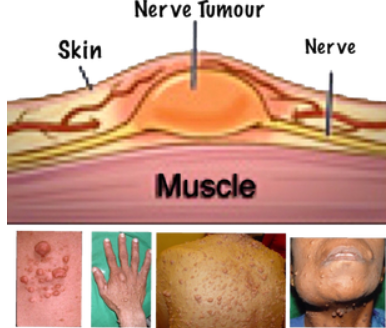
Many people ask, “What is neurofibromatosis?” after hearing the term from a doctor or reading about it online. Neurofibromatosis is a genetic disorder that affects the nervous system and causes tumors to grow along nerves in the body. These tumors are usually non-cancerous, but they can still lead to health complications depending on where they develop.
Because nerves are present throughout the body, this condition can affect different areas such as the skin, brain, spinal cord, and other organs. The severity varies widely from person to person.
What Causes Neurofibromatosis?
Neurofibromatosis is caused by a mutation in specific genes that control cell growth. These genes normally help prevent tumors from forming. When they do not function properly, cells can grow in an uncontrolled way, leading to tumor development.
The condition is often inherited from a parent who carries the altered gene. However, in many cases, it can appear in someone with no family history due to a new genetic mutation.
It is important to understand that neurofibromatosis is not contagious. It cannot spread from one person to another.
Types of Neurofibromatosis
There are three main types of this condition, and each one affects the body differently.
Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (NF1)
This is the most common type. It usually appears during childhood. Common signs include:
- Light brown skin patches called café-au-lait spots
- Small bumps on or under the skin
- Freckling in unusual areas like underarms
- Learning difficulties in some children
Most people with this type have mild to moderate symptoms.
Neurofibromatosis Type 2 (NF2)
This type is less common and often appears in teenage years or early adulthood. It mainly affects the nerves responsible for hearing and balance. Symptoms may include:
- Hearing loss
- Ringing in the ears
- Balance problems
Tumors often develop on the auditory nerves.
Schwannomatosis
This is the rarest type. It usually develops in adulthood and is known for causing painful tumors on nerves throughout the body. Unlike NF2, it does not typically affect hearing.
Common Symptoms
Symptoms vary depending on the type and severity. Some people experience only minor skin changes, while others may develop more serious complications.
Possible symptoms include:
- Skin spots or soft lumps
- Vision or hearing issues
- Bone abnormalities
- Headaches
- Chronic pain
Because symptoms can change over time, regular medical checkups are important.
How Is It Diagnosed?
Doctors diagnose neurofibromatosis through physical examinations, family medical history, and imaging tests such as MRI scans. In some cases, genetic testing is recommended to confirm the diagnosis.
Early detection helps doctors monitor tumor growth and manage complications before they become severe.
Treatment and Management
Currently, there is no complete cure for neurofibromatosis. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and preventing complications.
Options may include:
- Surgery to remove tumors causing pain or pressure
- Hearing devices for those with hearing loss
- Physical therapy
- Pain management strategies
- Regular monitoring by specialists
Each treatment plan is personalized based on the individual’s needs.
Living With Neurofibromatosis
Although it is a lifelong condition, many people with neurofibromatosis live active and productive lives. Support from healthcare providers, family members, and patient communities plays a major role in improving quality of life.
Education and awareness are powerful tools. Understanding what neurofibromatosis is can help individuals make informed health decisions and seek proper care.
Final Thoughts
So, what is neurofibromatosis? It is a genetic disorder that affects nerve tissue growth and can cause tumors to form along nerves in the body. While there is no cure yet, early diagnosis, regular monitoring, and proper treatment can help manage the condition effectively.