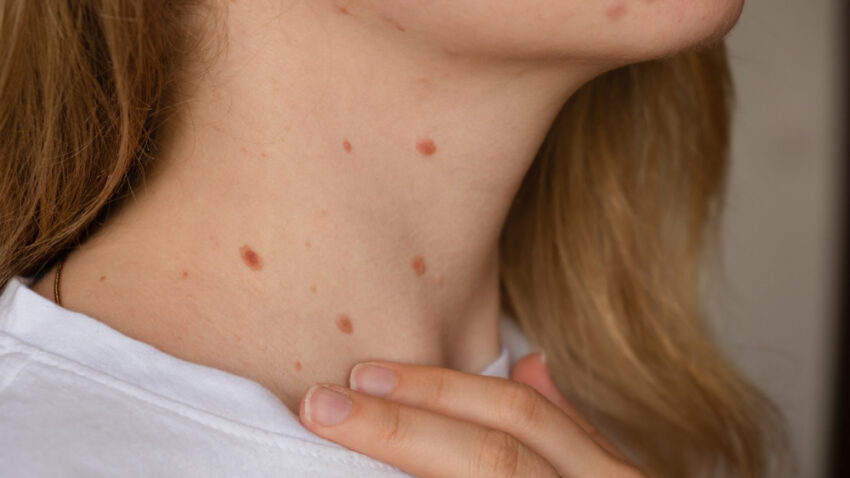
Skin tags are small, soft, benign growths that appear on the skin’s surface. Although they are generally harmless, many people wonder if they can spread from one person to another. Understanding the nature of these skin growths, their causes, risks, and methods of prevention is crucial for maintaining overall skin health. This article explores the essential aspects of skin tags, addressing the common question: Are Skin Tags Contagious?
What Are Skin Tags?
Skin tags, medically known as acrochordons, are tiny, flesh-colored growths that typically appear in areas where skin folds, such as the neck, armpits, groin, and under the breasts. They can vary in size, from a few millimeters to a few centimeters, and often hang from the skin by a thin stalk.
These growths are composed of collagen fibers, blood vessels, and sometimes fat cells. Despite their unusual appearance, skin tags are entirely benign and do not pose any direct health threat. They are different from warts, which are caused by viral infections and may be contagious.
Are Skin Tags Contagious?
One of the most frequently asked questions about skin tags is: Are Skin Tags Contagious? The short answer is no. Skin tags are not caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi, and therefore cannot be transmitted from person to person through physical contact, sharing clothing, or touching surfaces.
Unlike warts, which are caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV) and can spread through skin-to-skin contact, skin tags develop due to factors such as friction, genetics, hormonal changes, and aging. While they can appear in multiple areas on the same person’s body, there is no risk of infecting others.
Understanding this distinction helps alleviate unnecessary concerns and promotes better skin care practices without fear of contagion.
Causes of Skin Tags
While skin tags are harmless, knowing why they develop can help with prevention and management. The primary causes include:
-
Friction: Repeated rubbing of skin against skin or clothing often triggers the formation of skin tags. Common areas include the neck, underarms, and thighs.
-
Genetics: A family history of skin tags increases the likelihood of developing them.
-
Hormonal Changes: Pregnancy or hormonal imbalances can promote skin tag growth.
-
Age: Skin tags are more common in middle-aged and older adults due to changes in skin elasticity.
-
Obesity and Metabolic Conditions: Excess body weight or conditions like diabetes may increase the risk of skin tags.
Interestingly, maintaining proper health and wellness can indirectly reduce the likelihood of developing these growths by supporting healthy skin and weight management.
Risk Factors for Skin Tags
While skin tags themselves are not dangerous, certain factors may increase your susceptibility to developing them:
-
Obesity: Excess skin folds contribute to friction and the formation of tags.
-
Diabetes: Elevated blood sugar levels may be associated with more frequent skin tags.
-
Genetic Predisposition: Individuals with a family history of skin tags are more prone to them.
-
Pregnancy: Hormonal fluctuations can trigger skin tag growth, particularly in areas like the neck or under the arms.
Recognizing these risk factors allows individuals to take proactive measures to minimize their appearance or manage existing skin tags safely.
Signs That a Skin Tag Needs Medical Attention
Although skin tags are usually harmless, there are situations where a medical consultation is advisable:
-
Rapid Growth: A skin tag that grows unusually fast may require evaluation.
-
Pain or Discomfort: Tags that become irritated, itchy, or painful from friction or clothing should be checked.
-
Changes in Color or Shape: Any sudden changes could indicate other skin conditions, including benign or malignant tumors.
-
Bleeding: Persistent bleeding after minor trauma warrants medical attention.
Consulting a dermatologist ensures proper diagnosis and treatment, differentiating skin tags from warts, moles, or other skin lesions.
How to Prevent Skin Tags
While not all skin tags are preventable, certain practices can reduce the likelihood of their development:
-
Maintain a Healthy Weight: Reducing excess skin folds can minimize friction and tag formation.
-
Practice Good Hygiene: Keeping skin clean and dry reduces irritation and the chance of skin growths.
-
Wear Loose-Fitting Clothing: Tight clothing can rub against the skin, promoting tag formation.
-
Manage Chronic Conditions: Controlling diabetes and other metabolic disorders can indirectly lower risk.
-
Regular Skin Checks: Monitoring skin for new growths ensures early detection and treatment if needed.
By incorporating these habits into your daily routine, you can maintain healthy skin and reduce the occurrence of unwanted skin tags.
Treatment Options for Skin Tags
If skin tags are bothersome or unsightly, there are several safe treatment options:
-
Cryotherapy: Freezing the skin tag with liquid nitrogen, causing it to fall off.
-
Excision: Surgical removal using sterile scissors or a scalpel.
-
Ligation: Tying off the base of the skin tag to cut off blood supply, causing it to fall off naturally.
-
Over-the-Counter Remedies: Some creams and solutions are marketed for skin tag removal, though results vary.
It is essential to avoid home remedies that involve cutting or burning without professional guidance, as these can lead to infection or scarring.
Myths and Misconceptions About Skin Tags
There are several common myths surrounding skin tags, which can create unnecessary concern:
-
Contagion Myth: As mentioned, skin tags are not contagious, unlike warts caused by HPV.
-
Cancer Risk: Skin tags are benign and rarely, if ever, become cancerous.
-
Home Removal Safety: DIY methods such as cutting with unsterilized tools or applying harsh chemicals can cause infection and scarring.
By debunking these myths, individuals can approach skin tag management calmly and safely. Education and awareness are key to understanding these harmless growths.
Conclusion: Key Takeaways About Skin Tags
In summary, Are Skin Tags Contagious is a question many people ask out of concern for personal and family health. The answer is clear: skin tags cannot spread from person to person. They are benign growths caused by friction, genetics, age, hormonal changes, and metabolic conditions, not infections.
Understanding risk factors, signs for medical attention, prevention strategies, and safe treatment options allows individuals to manage skin tags effectively. Maintaining proper health and wellness plays a supportive role in preventing excessive skin growths.
By staying informed and consulting healthcare professionals when necessary, you can ensure healthy skin without undue worry about contagion or serious health risks. Skin tags are a common, harmless part of life for many adults, and with the right approach, they can be managed safely and effectively.